ABSTRACT:
Phages are also known as bacteriophages which are
normally viruses that infect and replicate within the bacteria. Phage therapy
is the clinical use of these bacteriophages to treat infections caused by
superbugs (bacteria that have acquired resistance against antibiotics). Phages
when administered in to bacteria, causes the lysis of the bacterial cells in
the lytic phase of phage life cycle. Phage therapy has acquired it’s importance
in the recent years after their successful use in managing some life threatening
infections and helped in saving lives. Phage therapy is currently being used as
the antimicrobial therapy in some western countries.this paper mainly discusses
about using phage therapy in treating infections caused by superbugs, and also
discusses on what measures should be taken by different countries to
successfully introduce the phage therapy in clinical use. We conclude that
phage therapy can be the best alternative for treating infections caused by
superbugs, where antibiotics can’t work.
Key-Words: bacteriophages, replicate, superbugs, resistant,
lytic phase, antimicrobial, therapy.
INTRODUCTION:
Phages are also known as bacteriophages which are normally viruses that infect and replicate within the bacteria. Phages were first discovered by Frederick W. Twort (1915) and also by Félix d'Hérelle (1917). In 1920 some scientists and physicians used phages in humans for treating various bacterial infections when antibiotics were not yet discovered. Later phages therapy was promoted by F.dHerelle who used to travel many countries and helped others on how to use phage therapy in humans. In 1940 phages have lost their importance due to the discovery of antibiotics. G. ELIAVA institute of bacteriophages in Georgia has never lost its interest on phage therapy, they never quit their research on phages till now. The researchers used to collect phages from Environment sources and store them in phage bank. This collection of phages by the ELIAVA institute has provided information on which phages can be selectively used against bacteria isolated for personalized therapies. However data from a single institute is not sufficient to approve medicines all over the world. Due to an increase in antibiotic resistance, it became very hard to treat bacterial infections, so the rest of the world along with G. ELIAVA institute has kept their interest in utilizing phage therapy for treating infections in humans caused by superbugs. To approve phage therapy as an effective alternative for antibiotics more data is needed which can be obtained by conducting more clinical trails. Previously conducted studies on phages have failed to provide sufficient information on the efficacy of the phages. So, phage therapy will not be approved by the FDA until it clears all the stages of clinical trials. Few studies have completed phase 1 trial but it is not enough to approve and to release into the market for human use. However, there are some situations where phages worked very effectively where antibiotics failed. These are abundant in nature and are present wherever the bacteria are found like soil, water, deep within the earth's crust. Oceans are a large source of phages it is estimated about 1030 bacteriophages in this world.
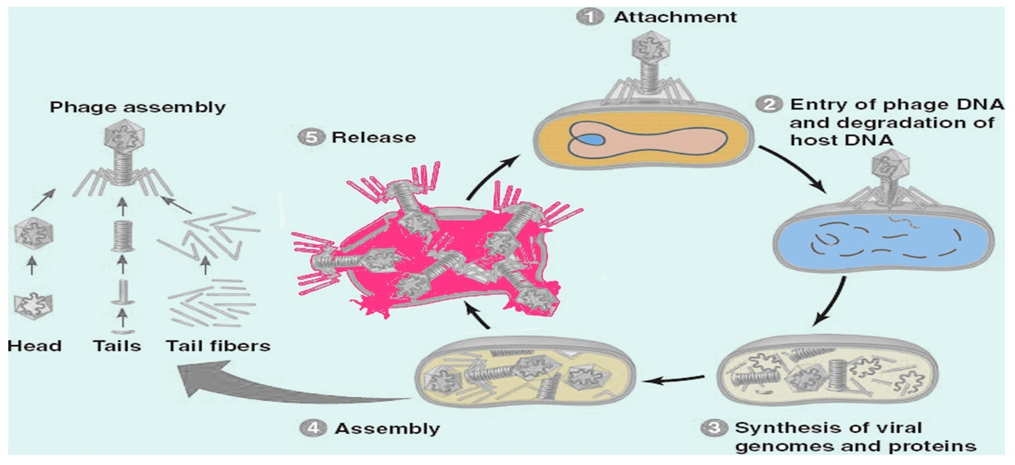
HOW DO THEY SHOW THEIR ACTION OVER BACTERIA?
There are
specialized protein-based enzymes and genes in their cells that are able to
degrade the cell wall of bacteria and lyse them. They originate from viruses
(phages) that live and attack bacteria. Lysin is produced by phages over
bacteria and stops proliferation. Firstly it gets attached to bacteria(host
cell), and the phage release the genome into the bacteria, and the DNA
replicate and new proteins are formed. And the new phages in bacterial cell (host) get
burst and undergo lysis. Bacteriophages generally attack bacteria that are
matched. The bacteria should be specific to phage. The bacteria will undergo
reproductions, it requires shelter and search for food but unlikely phages will
only go reproduction.
HOW DOES BACTERIA ACQIURE RESISTANCE?
Due to improper and long term use
of antibiotics, Microbes tend to evolve resistance against antibiotics.
Resistant bacteria have defense strategies that protect them from antibiotics.
·
Restrict access to the antibiotics: By limiting the
number or reducing the size of openings in cell-walls. Due to reduction in
number or size of cell wall pores sufficient amount of antibiotics can’t enter
into bacteria.
·
Get rid of antibiotics: Some bacteria can use pumps
present in their cell walls to push out antibiotic that is entering into it.
·
Destroy the antibiotic: Some bacteria uses enzymes to
break down the antibiotic drug and make them inactive. Eg:beta-lactamase.
·
Change the antibiotics: Some bacteria uses enzymes to
alter the antibiotics and make them inactive.
· Bypass the effect of antibiotics: some bacteria changes the composition or the structure of target in them, this can stop the antibiotics from binding with the target and makes ineffectiveness.
Phage therapy is an alternative or supplementary therapy for eradicating superbugs
TYPES OF PHAGES AND THEIR HOSTS
|
S.NO |
PHAGE |
EFFECTIVE AGAINST (HOST) |
|
1 |
Escherichia virus T4 |
E.coli |
|
2 |
M13 is a filamentous bacteriophage |
E.coli |
|
3 |
MS2 bacteriophage |
E.coli and some enterobacteriaceae |
|
4 |
Entero-bacteria phage T2 |
E.coli |
|
5 |
Φ6 (Phi 6) |
pseudomonas bacteria |
|
6 |
Bacteriophage T5 |
E.coli |
|
7 |
Filamentous bacteriophage fd |
E.coli |
|
8 |
ΦX174 |
E.coli |
|
9 |
Lipothrixviridae |
Archea: acidianus |
|
10 |
Plasmaviridae |
Acholeplasma species |
|
11 |
Bicaudaviridae |
hyperthermophilic archaea) |
|
12 |
Guttaviridae |
hyper thermophilic archaea |
|
13 |
Aeropyrumpernix bacilliform virus |
won’t cause host cell lysis |
|
14 |
φkm18p |
Acinetobacter baumannii |
|
15 |
Bacillus phage phi29 |
|
FIGHT AGAINST MULTI-DRUG RESISTANT BACTERIA
WHO
has given a list of 12 species of bacteria by priority based on their level of
resistance. Now the bacteria get resistance beyond the level of Anti-biotics.
The very serious issue is to face multiple drug-resistant bacterial infection.
So, here the only one that can fight against MDR bacteria is phages. These
phages are found next to bacteria. Now we focus upon 4 high-level risk
pathogens, Acinetobacter baumannii, pseudomonas aeruginosa, members of
Enterobacteriaceae, Clostridium difficile.
Phage therapy
against few pathogens.
Acinetobacter
baumannii:
Acinetobacterbaumannii is a high level drug resistance
pathogen and it also cause hospital infections. In past 20 years
backA.baumanniihas been introduced in mice, the results obtained is the
increase survival in the phage treated group compared to controls. Endolysins
which are produced by the A. baumannii has capacity to kill the MDR bacteria and
rescue mice from lethal. Lysin(or)endolysinsare the hydrolytic enzymes which
will help to cleavage the MDR bacteria cell wall. Although, the lysinwon’t work
in the gram negative bacteria .A. baumannii infects humans which lead to cause
pancreatic pseudocyst infection, this was happened in USA person name was
petterson. All antibiotics are failed in front of it. The alternative treatment
was to start phage therapy .So, the first IV administration of phage treatment
to this patient. ThisAcinetobacterbaumannii will also infect in surgical cuts
like Craniectomy site , after infection of Acinetobacter baumannii they have
started cocktail of three bacteriophages to improve patient quality of life.
Enterobacteriaceae:
In this family, they are some familiar pathogens such
as Klebsiella, shigella, E.coli, salmonella, Enterobacteria,citrobacter. Among
them high MDR are E.coli and Klebsiellasps, Enterobacteriaserratia, proteussps.
The phages which involved in killing the E.coli are known as Coliphages. E.coli
mostly seen in both Internal and External Intestinal pathogens. If the two
types pathogens are combined to form Infection are called as biofilm associated
infection. Which are also killed by the Coliphages. These biofilm associated
infections are occurred by unsterilized medical devices and by the nosocomial
infection. Cao et al. conducted a trail on mice which is infected
administration of phages and in reduce the severity and the low cytokines
levels in lungs. Liposome loaded phage cocktail is help in healing the
infectious condition. To overcome , the gram negative resistance , research had
combined protein with receptor binding domains of colicin A to a E.coli.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa:
This infection will develop in persons who are
hospitalized. The persons who are having cystic fibrosis will develop the
chronic lung infection. Although the researchers are done back 50 years ago ,
phage therapy on the p.aeruginosa but now the things has changed. So, further
studies should conduct as both the mucoid and non- mucoid p. aeruginosa. The
immunity in humans are completely normal when the phage therapy has introduced
to humans. Positive outcomes are observed in patients who are treating with phage therapy. There is no limitation in
cocktail phages like mix of 3 but also mix of 6 cocktail phages are introduced
in treating the lung infection of p.aeruginosa in mice. In case study of aortic prosthetic graft infection by aeruginosa.
So, here treatment is given as combinational of
phages and ceftazidime was the best and successful treatment to treat
this MDR pathogen.
Vibrio cholera:
It spreads by water,it will cause serious dehydration
Diarrhoeal condition. To prevent this
Condition WHO have Conducted oral cholera vaccines and it try to create
awareness of sanitation and hygiene practice. Even through, there is still
observing the cholera symptomatic patients. WHO didn’t gave approval of the
prophylactic treatment of cholera because there is a chance of developing drug
resistance bacteria. It may leads patient may develop resistance to drug and
bacterial infection won’t be cured. But, here the phages are shown more
significant action than antibiotics in treating this. 3 cocktail phages are
included in treatment of V.cholera ICP1,ICP2,ICP3. In these phages ICP1.ICP 2
shows the complete action in treating Vibrio because they are having (LPS) O
Antigen. ICP 3 act as partial (LPS) O Antigen.
AT WHICH STAGE WE HAVE TO IMPLEMENT PHAGE THERAPY ?
The
phage therapy includes the virulent pathogens, which are dangerous weapons
released to kill the bacteria. The MDR bacteria are dangerous to human body
cells which make the person ready to die. There, is no particular stage to
introduce or to implement phage therapy, this happens when the given
anti-biotics are failed to do their work. The bacteria are going on updated
based on morphology and their mechanism skills. So, the phages are the best
step to look forward to kill the MDR bacteria. It can be given by single phage
(or) 3,6 cocktail of virulent pathogens. The researchers have also combined the
phage with anti-biotics. They should be matched with the respective MDR
bacteria.
CONCLUSION:
As
multiple drug resistance bacteria cases are can’t be treated with antibiotics.
It becomes very challenging for physicians to treat infections with an
Antibiotic. So some of the researchers and scientists are recalling their
interest in phage therapy since phage therapy is not new and is being used in
some countries of union soviet. so phage therapy can be the best alternative to
antibiotic therapy for treating infections caused by superbugs. As the data
obtained is only about how well the phages are useful, we need to collect more
data on the safety, adverse effects and interactions by conducting clinical
studies and to approve their use in humans. The phage therapy should spread all
over the world like Anti-biotics.





.webp)

0 Comments